Mastopexy Lugano
Mastopexy is a surgical operation indicated to correct the shape and displacement of the breast below the breast fold; this dislocation is known as breast ptosis, is measured in centimeters and can affect the mammary gland (glandular ptosis), the nipple-areola complex (cutaneous ptosis) or both. If the breast volume is insufficient, a prosthetic implant can be associated.
Informazioni sulla mastopessi
Mastopexy surgery must be planned in conditions of weight and hormonal stability in relation to pregnancies and breastfeeding.
Intervention in day hospital
Breast ptosis is a frequent pathology, which can have a significant psychological and emotional impact. Ptosis can be caused by weakness of the ligament (Cooper) that suspends the gland, by a low percentage of collagen in the dermis with the appearance of stretch marks, by aging, by weight changes, by post-pregnancy and post-breastfeeding involution, by eating disorders and smoking.

- Duration
- 150 mins
- Discharge
- 4/5 hours
- Complete recovery
- 24 hours
Operating room mastopexy
Before mastopexy surgery
Mastopexy is an operation that requires an accurate pre-operative specialist visit during which the surgeon will evaluate the patient's requests, the condition of the breasts, choose the shape and size of the breast suited to the biometric parameters and the surgical procedure best suited to the case.
If the breasts are small and sagging but have not lost volume, it may be sufficient to proceed with a mastopexy. If, however, the sagging breast has lost all or part of its volume or is very large, it is advisable to perform a mastopexy associated, respectively, with an additive mammoplasty or a reduction mammoplasty to restore shape, volume and firmness.
During mastopexy surgery
The procedure of mastopexy surgery does not differ much from that of reduction mammoplasty. No glandular tissue is removed which is instead entirely preserved and modeled with internal incisions and sutures. The excess skin is eliminated; if the ptosis is not excessive it can be corrected by leaving only a circular scar around the areola, "Round-Block".
An internal support is made from the patient's tissues which fixes and stabilizes the residual breast mass to the pectoralis major muscle. This support performs the function of a sturdy ligament which on the one hand permanently suspends the breast, and on the other prevents its weight from weighing on the scars which, not being subjected to tension, are of good quality and can be limited, even for significantly larger breasts. relaxed and large in volume, with a periareolar scar and a vertical scar from the areola to the breast fold.
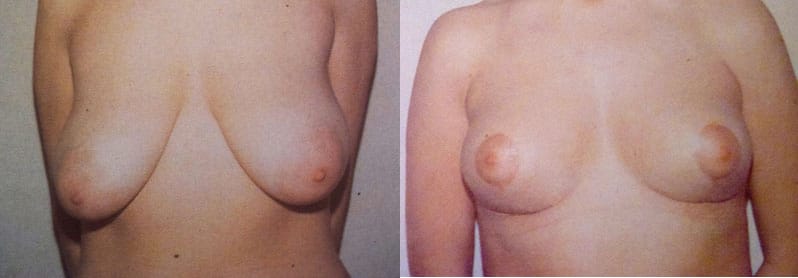
Mastopexy surgery before and after
After mastopexy surgery
Starting from the third day after the operation it is possible to resume a normal life.
Three weeks after mastopexy surgery it is possible to resume sporting activities. The result of a mastopexy operation is good and long-lasting thanks to the internal support. Lactation is preserved. For a stable result you need to wait 2/3 months.
How much does a mastopexy cost?
The cost of mastopexy surgery can vary based on the patient's requests and the initial situation.
Personalized financing.

